What is Diabetes ?
Diabetes is a disorder where the body does not produce insulin or it is inadequate to be used effectively. There are three types of diabetes types :
Type 1 diabetes mellitus,
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
Gestational diabetes mellitus [diabetes in pregnancy].
Classification
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus [T1D]
 Type 1 diabetes, once known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin. Insulin is a hormone needed to allow glucose / sugar to enter cells to produce energy. Although type 1 diabetes usually appears during childhood or adolescence, it can develop in adults as well.
Type 1 diabetes, once known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin. Insulin is a hormone needed to allow glucose / sugar to enter cells to produce energy. Although type 1 diabetes usually appears during childhood or adolescence, it can develop in adults as well.
Acceptance of diagnosis is difficult as you need to inject insulin and check your blood glucose levels [BGL] several times a day for the rest of your life. Acceptance of the illness is vital to achieve good control. If you are anxious or stressed about it, your BGLs will remain high.
Treatment focuses on maintenance of good BGL through proper diet, adequate exercise and stress. Good control is vital to prevent complications.
There is no cure and the causation unknown.
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus [T2D]
 Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes as your body either resists the effects of insulin [a hormone that regulates the movement of sugar into your cells] or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose/ sugar levels.
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes as your body either resists the effects of insulin [a hormone that regulates the movement of sugar into your cells] or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose/ sugar levels.
You can get T2D at any age. A grandparents disease has now become a grandchild’s illness with the marked reduction in the age of onset as more and more young persons even children and adolescents are diagnosed with T2D.
T2D is a lifestyle illness and treatment rests on correction of unhealthy lifestyles. Treatment focuses on proper diet, high in fibre and low on carbohydrates, adequate exercise and reduction of stress.
The causative factors are multiple and interaction produces the condition. The factors are Genetics, Fetal Origins [in the womb] Lifestyles and Stress.
Though there is no cure, prevention is possible through healthy lifestyles i.e. proper nutrition, regular exercise and reduction of stress.
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus [GDM] -Diabetes in Pregnancy
GDM is a form of diabetes consisting of high blood glucose levels during pregnancy. Good control of BGL is essential to avoid complications both in mother and child. GDM usually appears around 28th week and disappears after pregnancy. However, it increases the risk of developing T2D in later life in both mother and child. Approximately 50% of person with a history of GDM develop T2D within 5 – 10 years after delivery.
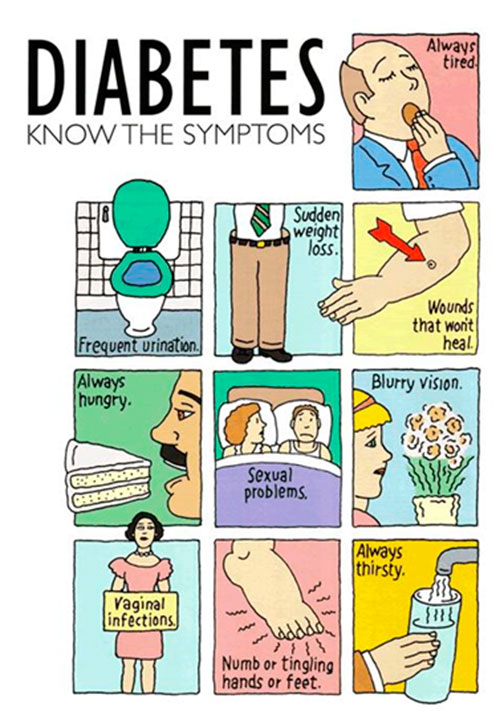
Symptoms
- Loss of weight
- Excessive urination
- Excessive thirst
- Feeling tired , sleepy and or drowsiness
- Blurred vision
- Itching dry skin especially in the genital area
- Infections and slow healing wounds
- Excessive hunger
- Ants around the commode or urinals